Definitions of Informal Learning
The notion of informal learning is becoming increasingly important. In a corporate context, learning is much more than formal training. And, our academic learning also comes from different informal channels; e.g. through games, simulations, experiments, story-telling, discovery. Outside the classroom boundaries, we use Google, communicate with peers, join online communities, work on problems together, share learning resources etc. Actually I don´t like the distinction made between formal and informal learning. It´s all about learning. Whether it comes through formal or informal means, it doesn´t matter. I believe we should blend formal, informal learning, and knowledge management into one integrated solution that places the learner/knowledge worker at the center and gives him/her the control over the learning experience. The primary goal is to enhance the personal and professional performance and increase the ability of any individual, project team, or organisation to cope with the demands of the new knowledge intensiv era.
In this post, I´m trying to compile a list of definitions of informal learning. The list is far from being complete and will be updated regularly. Please let me know if you find or have your own definition of the same.
- Jay Cross writes "At work we learn more in the break room than in the classroom. We discover how to do our jobs through informal learning -- observing others, asking the person in the next cubicle, calling the help desk, trial-and-error, and simply working with people in the know. Formal learning - classes and workshops and online events - is the source of only 10% to 20% of what we learn at work".
- Marcia Connor states "Informal learning accounts for over 75% of the learning taking place in organizations today. Often, the most valuable learning takes place serendipitously, by random chance".
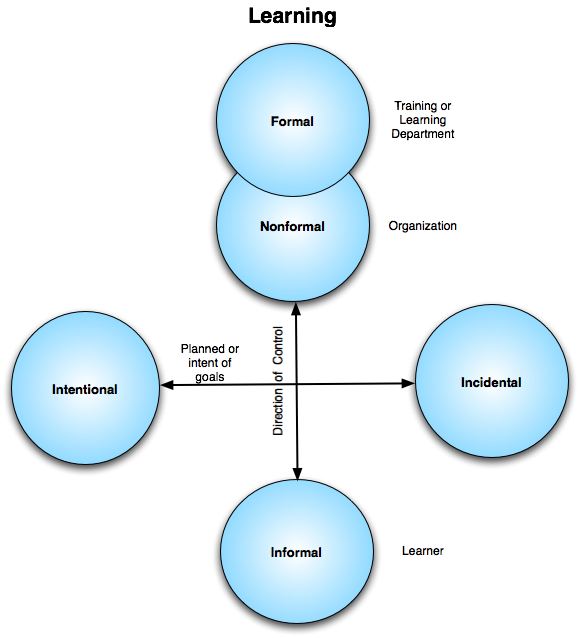
- Juliette White notes "The degree of informality of learning is the degree to which you haven’t been told what to do i.e. informal learning by definition can only be influenced by creating an environment and not by direct instruction".
- Graham Attwell cites "Helen Colley, Phil Hodkinson and Janice Malcom have undertaken an extensive review of literature on informal learning. In the review they identified eight different theoretical models of informal or non formal learning. They suggest the following factors as being common in many if not all of the definitions:
- Process. This includes learner activity, pedagogical styles and issues of assessment: that is, the learning practices, and the relationships between learner and others (tutors, teachers, trainers, mentors, guides).
- Location and setting. Is the location of the learning within a setting that is primarily education, community or workplace? Does the learning take place in the context of: fixed or open time frames; is there specified curriculum, objectives, certification; etc.
- Purposes. Is the learning secondary to other prime purposes, or the main purpose of itself? Whose purposes are dominant – the learner’s, or others’?
- Content. This covers issues about the nature of what is being learned. Is this the acquisition of established expert knowledge/understanding/practices, or the development of something new? Is the focus on propositional knowledge or situated practice? Is the focus on high status knowledge or not?".
- Stephen Downes writes "What makes informal learning different from formal learning is not that it is formless, but rather, it that it is conducted outside the domain of the formal education infrastructure, with the associated and not trivial implication that it is managed by the learner, and not the professor or institution".
- "The learning zone is the convergence of formal and informal learning within a social context where the interests of the enterprise and individual meet. The role of social networks is essential to successful learning in enterprises. We know that 70 to 90 percent of learning is informal, a combination of personal reflection and social exchange with trusted. Extracurricular IS the curriculum. Why leave the potential benefits of informal learning to chance? Companies are becoming more strategic in their approach to learning as they shift focus to informal, experiential aspects of employee development".
- Donald Clark states "rather than learning being organized around an event, it becomes a network of both planned and spontaneous situations. Some business processes are just too important to be left to chance. For example, manufacturing a product to specifications or safety procedures normally require that some type of formalized learning be given. Yet, it does not require strictly formalized learning methods. Competencies require the mastery of the 5 Cs: Content, Conversation, Connectivity, Collaboration, and Context.
- While we all enjoy a good speaker, literature, or video that a well prepared lesson can provide, we also need to create and search for our own content in order to provide meaning to the new information.
- While corporate classrooms have been moving away from lectures and more towards the interactive, it is often only after the learners have left the classroom and have had a chance to digest and reflect on their new knowledge and skills that they are able to engage in meaningful conversations with others to make their learning deeper.
- People are social creatures, thus many of them look forward to the social aspects that a well prepared class can provide, yet once they leave the classroom, technologies such as the web, blogs, discussion groups, mobile phones, and email allows them to connect not only with the people they met in class, but also with others who share the same interests.
- This social aspect carries over to working and learning with others in new projects that allows them further gain insight into their recently acquired knowledge and skills.
- And finally, it is the experiences provided by the other four Cs that give the learners a more well rounded picture or context -- information only becomes relevant when it is related to something the learner is already familiar with."
Interesting posts and articles about "Informal Learning":
- Informal Learning - the other 80% (Jay Cross)
- Informal Learning (Marcia Connor)
- Definitions of informal learning (Juliette White)
- Formal or informal - does it matter - its all learning (Graham Attwell)
- The Form of Informal - The Form of Informal 2 (Stephen Downes)
- More on the Form of Informal (Tony Karrer)
- Convergence Learning (Donald Clark)


No comments:
Post a Comment